Trending Stories 3 years ago
Biometric Technology and its Role in Law
Faced with pressing concerns of document fraud, identity theft, terrorism and cybercrime, biometric technology and its many applications have become indispensable to everyday life
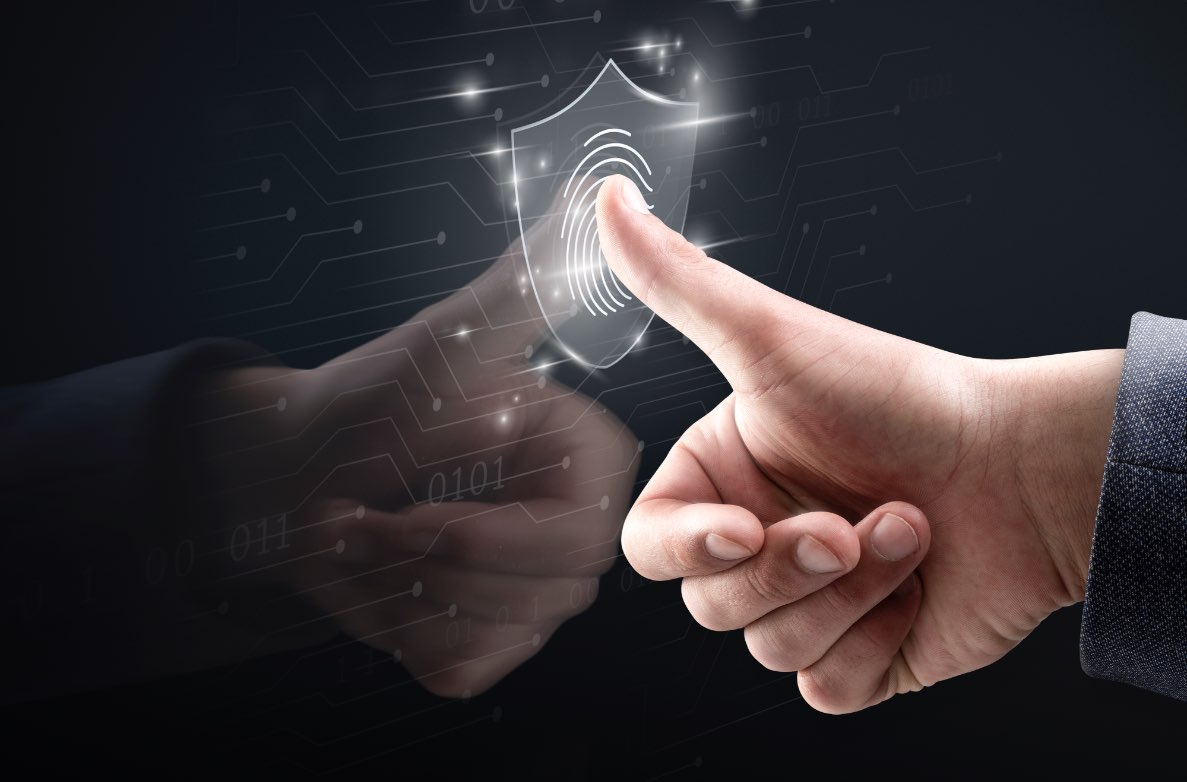

When they first emerged as a revolutionary stem in technological advancements, Biometric Technology was marketed as ‘the most practical means of identifying and authenticating individuals in a reliable and fast way’. They addressed the longstanding concern to prove one’s identity, irrefutably, by using the particular markers that make human beings unique. Today, faced with pressing concerns of document fraud, identity theft, terrorism and cybercrime, biometric technology and its many applications have become indispensable to everyday life.
In the outset, there are two broad types of biometric information:
1. Physiological measurements: that include morphological and biological data like fingerprints, facial details, iris/retina data, blood, saliva and DNA.
2. Behavioural measurements: that include more nuanced traits like voice recognition, signature and handwriting analysis, gait, step sounds, and gestures.
Different techniques of storing and analysing biometric information are constantly subjected to further research and are constantly being improved upon. Their significance within different sectors of society has been just as widespread.
· Biometric technology has long been widely used in law enforcement. From finger and palm prints to facial recognition (mug shots), they have been in use in several criminal id solutions. Today, Automated Biometric Identification Systems can create and store biometric information that match biometric templates for the face, finger, and iris.
· Although much is unknown about how defence agencies around the world use biometric data, several declassified reports have proven that military agencies have been accumulating extensive biometric information and have been using it to identify personnel on the battlefield.
· While most of us are familiar with e-passports, their new and improved versions, unsurprisingly named ‘Biometric Passports’, have completely revolutionised border control, travel and migration. Equipped with fingerprints and passport photos, they have completely automated border control.
· Automated biometric identification systems are being used increasingly by countries across the world to ensure civil identities, population registration and voter registration. Closer to home, the Aadhar card has successfully bio-tagged the largest democracy in the world!
From unlocking phones, doors and lockers to identifying known suspects from comprehensive databases, human identity markers have been extensively and categorically catalogued using technology. Not only does biometric technology greatly reduce the time and effort involved in accurate identification processes but it also lends to a highly responsible security system and an extremely efficient attendance management solution – all without burning holes into pockets. Their sophistication, deftness and hyper-accuracy have greatly impacted the way institutions and countries function and ultimately succeed.